Fundamentals of CNC Programming

What is CNC Programming?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) programming is the process of telling a machine how to move, cut, drill, or shape material using a written set of instructions.
Instead of manual levers and wheels, we feed the machine a program that controls:
✅ Tool paths (X, Y, Z movement)
✅ Cutting speeds and feeds
✅ Start/stop commands for spindle and coolant
✅ Repetitive cycles for drilling, turning, or milling
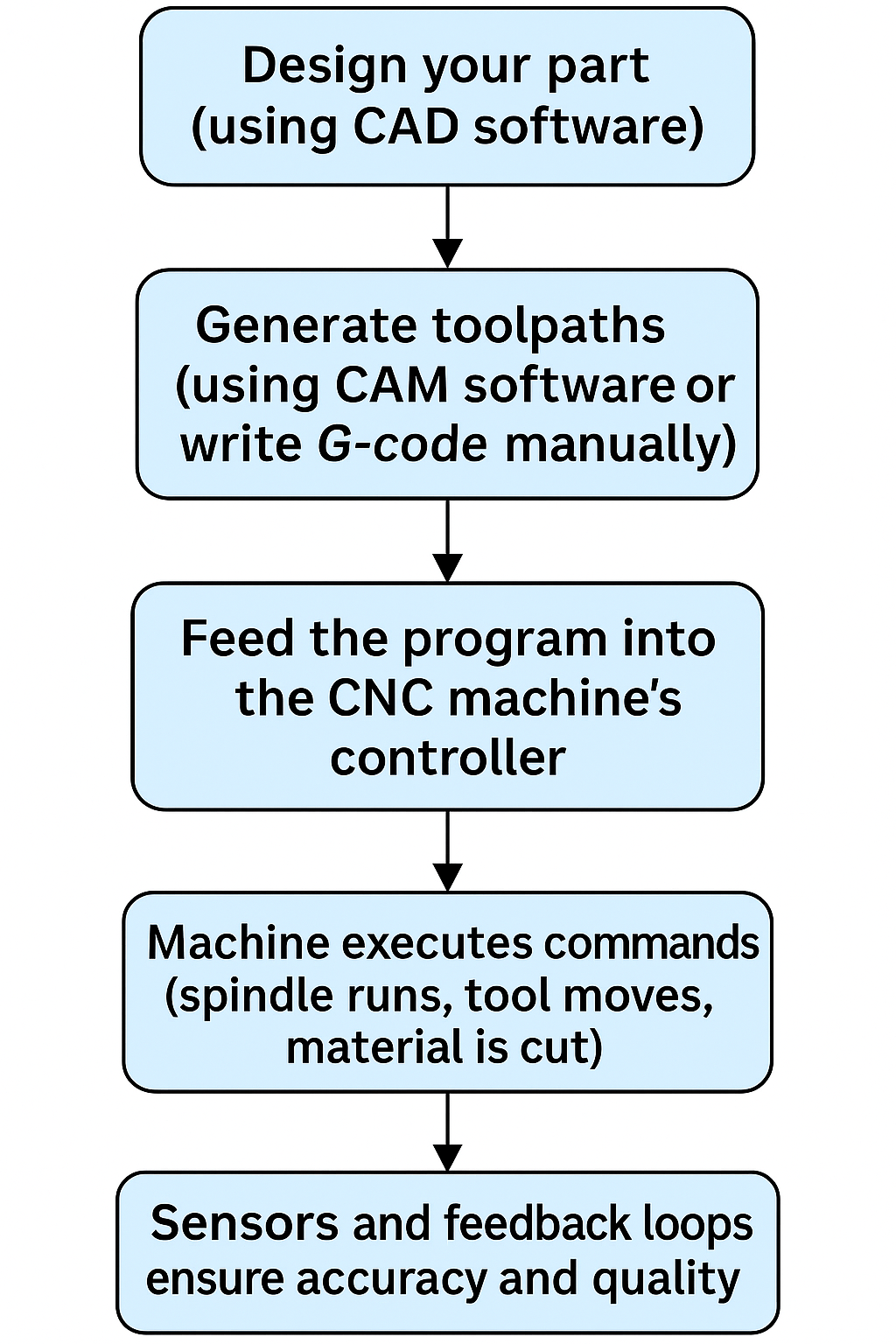
How CNC Works
How to Do CNC Programming?
CNC programming is a vital aspect of the CNC machining process. It involves using the G-code language to describe the shape, process, parameters, and auxiliary information of a part. The CNC programmer writes the program using specific function instruction codes and block formats.
CNC programming can be done manually or automatically, depending on the complexity of the part. Manual programming requires the programmer to have in-depth knowledge of the G-code language and the ability to input the instructions accurately. Automatic programming methods, on the other hand, rely on advanced software that can generate CNC machining programs automatically. These methods are particularly efficient and reliable for parts with complex shapes.
Manual CNC Programming
In manual CNC programming, the programmer manually writes the program using the G-code language. They analyze the part requirements, determine the processing route, select the appropriate process parameters, and calculate the tool position data. The programmer must have a thorough understanding of the CNC machining principles, coordinate systems, program structure, and common CNC instructions.
Automatic CNC Programming
Automatic CNC programming utilizes computer software to generate CNC machining programs automatically. The software takes into account the part design, material, and specific machining requirements to create an optimized program. This method is highly efficient and reliable, especially for parts with intricate geometries and non-circular curve profiles.
What is a G-code?
G-code is short for “geometric code” – a language that tells the CNC machine how to move. It directs where the tool starts, what path it takes, and at what speed (feed-rate), shaping the workpiece through precise instructions.
Basic G-codes
- G00: Rapid positioning (Tool moves to specified coordinates rapidly without cutting)
- G01: Linear interpolation (Tool moves in straight line while cutting)
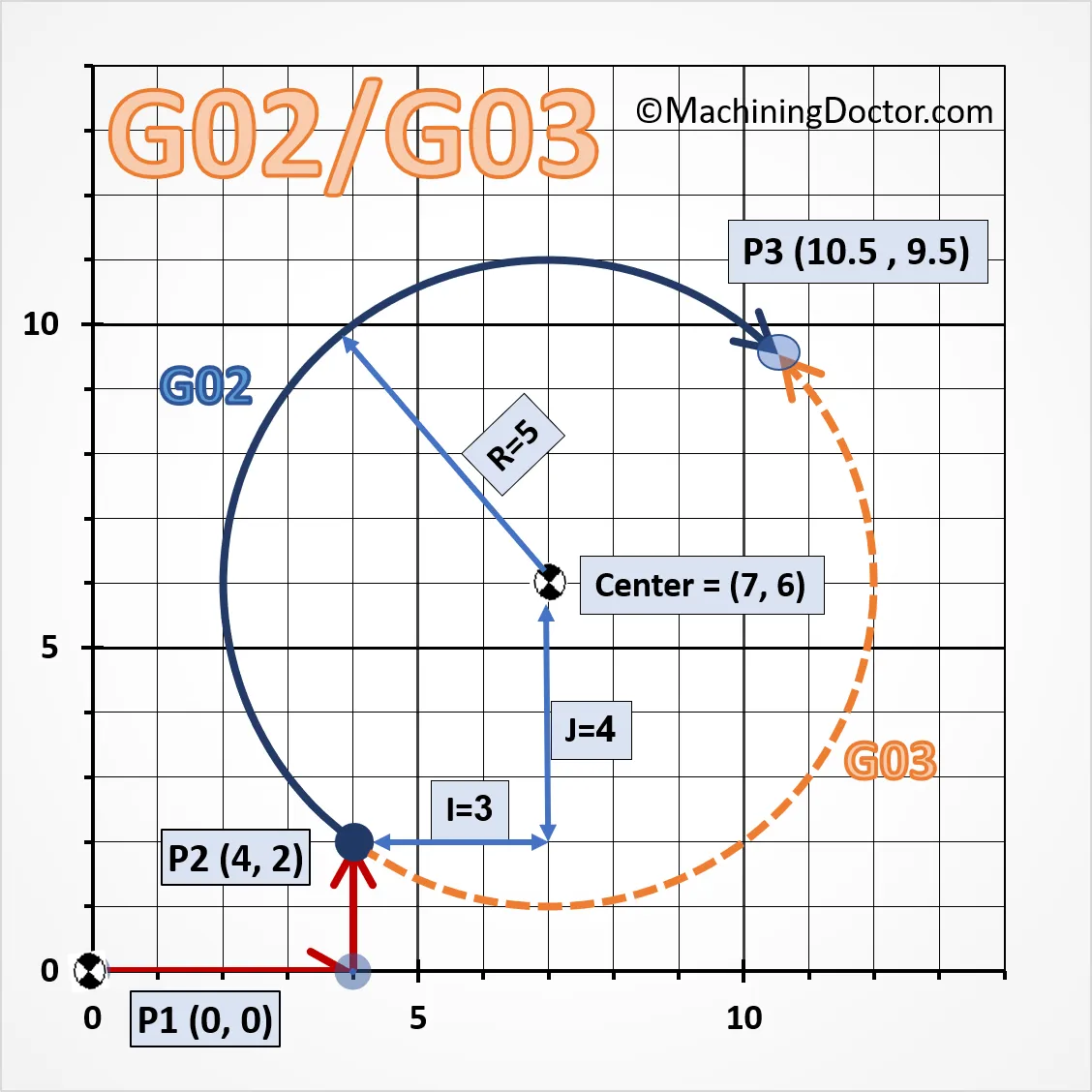
- G02: Circular interpolation clockwise (CW) (Tool cuts in clockwise circular motion)
- G03: Circular interpolation counter-clockwise (CCW)
- G20: Inch input (in.)
- G40: Cutter compensation cancel
- G41: Cutter compensation left
- G42: Cutter compensation right
- G43: Tool length compensation positive (+) direction
- G44: Tool length compensation minus (-) direction
- G49: Tool length compensation cancels
- G90: Absolute programming
- G91: Incremental programming
What is a M-code?
M or miscellaneous codes are used to either turn ON or OFF different functions, which control certain machine tool operations.
Basic M-codes
- M00: Program stop
- M02: End of program
- M03: Spindle start (forward CW)
- M04: Spindle start (reverse CCW)
- M05: Spindle stop
- M06: Tool change
- M08: Coolant on
- M09: Coolant off
- M98: Transfer to subprogram
- M99 End of subprogram
Learning CNC Programming With Example
Resources for further study