20251GTY5: Smart Chessboard
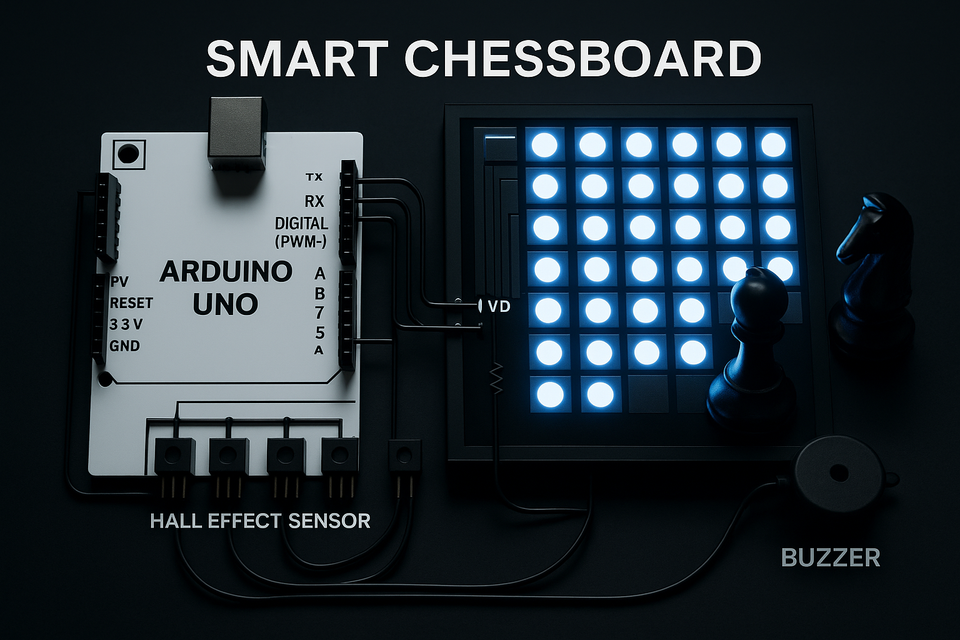
Brief Description & Functionality
A Smart Chessboard is an interactive, sensor-enabled electronic chess system that automatically detects piece positions, validates moves in real-time, provides move suggestions, and enables both local and online gameplay. This technology bridges traditional physical chess with digital platforms, offering enhanced learning capabilities, game analysis, and remote multiplayer functionality.
The system serves multiple purposes:
- Real-time move detection and validation using embedded sensors
- Interactive learning assistance with LED move indicators and AI suggestions
- Online connectivity for remote gameplay against opponents worldwide
- Game recording and analysis with automatic move notation and storage
- Educational features including hint systems and strategy improvement tools
- Tournament integration for broadcasting and official game recording
Key benefits include enhanced learning experiences for beginners, convenient practice against AI opponents of adjustable difficulty, seamless integration with popular chess platforms like Chess.com and Lichess, and the ability to maintain the tactile experience of physical chess pieces while gaining digital advantages.
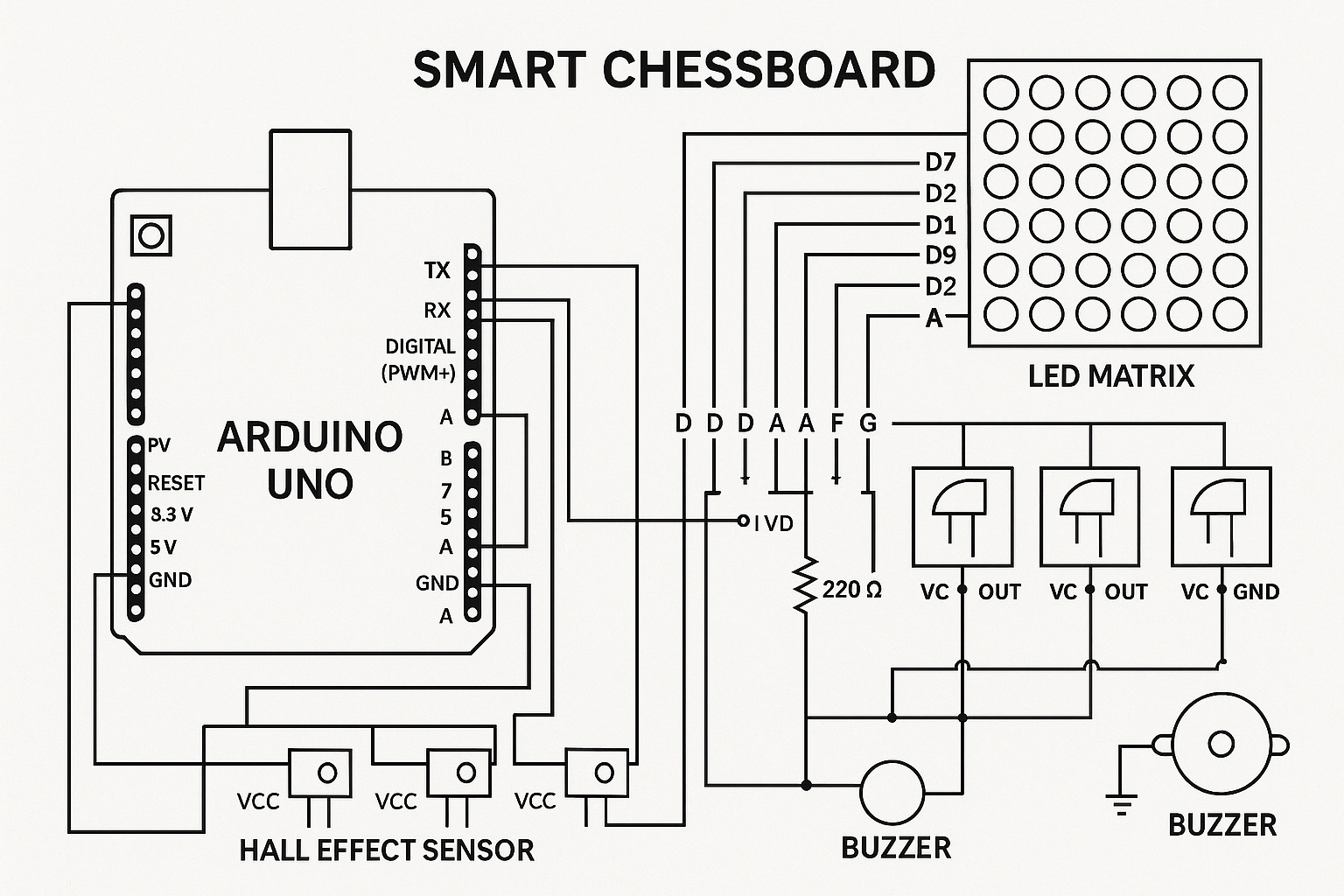
Working Principle:
The system operates through a sophisticated detection and feedback loop:
- Sensor Detection: Each of the 64 squares contains either Hall effect sensors or reed switches that detect chess pieces equipped with embedded magnets. When a piece is placed on or removed from a square, the sensor immediately registers the change.
- Move Processing: A microcontroller (typically Arduino) continuously scans the sensor matrix, comparing current board state with previous positions to identify moves. This data is processed to determine move validity and game progression.
- Visual Feedback: RGB LED arrays beneath each square provide immediate visual feedback - highlighting legal moves when a piece is selected, indicating captured pieces, showing opponent moves, and displaying game status through different colors and patterns.
- AI Integration: A secondary computer (often Raspberry Pi) runs chess engines like Stockfish, providing move suggestions, game analysis, and AI opponents. This system can also interface with online chess platforms for remote play.
- Communication: Bluetooth or USB connectivity enables the board to communicate with computers, smartphones, or online chess platforms, allowing for digital game recording and internet-enabled multiplayer matches.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensor Array | 64 Hall effect or reed switch sensors detect magnets in chess pieces |
| LED Matrix | RGB LEDs under each square for move indication and visual feedback |
| Microcontroller | Arduino processes sensor data and controls LED responses |
| Single Board Computer | Raspberry Pi handles AI, online connectivity, and advanced features |
| Control Interface | Physical buttons and OLED display for game control and information |
| Power Management | USB-powered system with optional battery backup for portability |
| Chess Pieces | Standard pieces modified with embedded neodymium magnets |
| Board Structure | 3D-printed or wooden frame with integrated electronics and wiring |
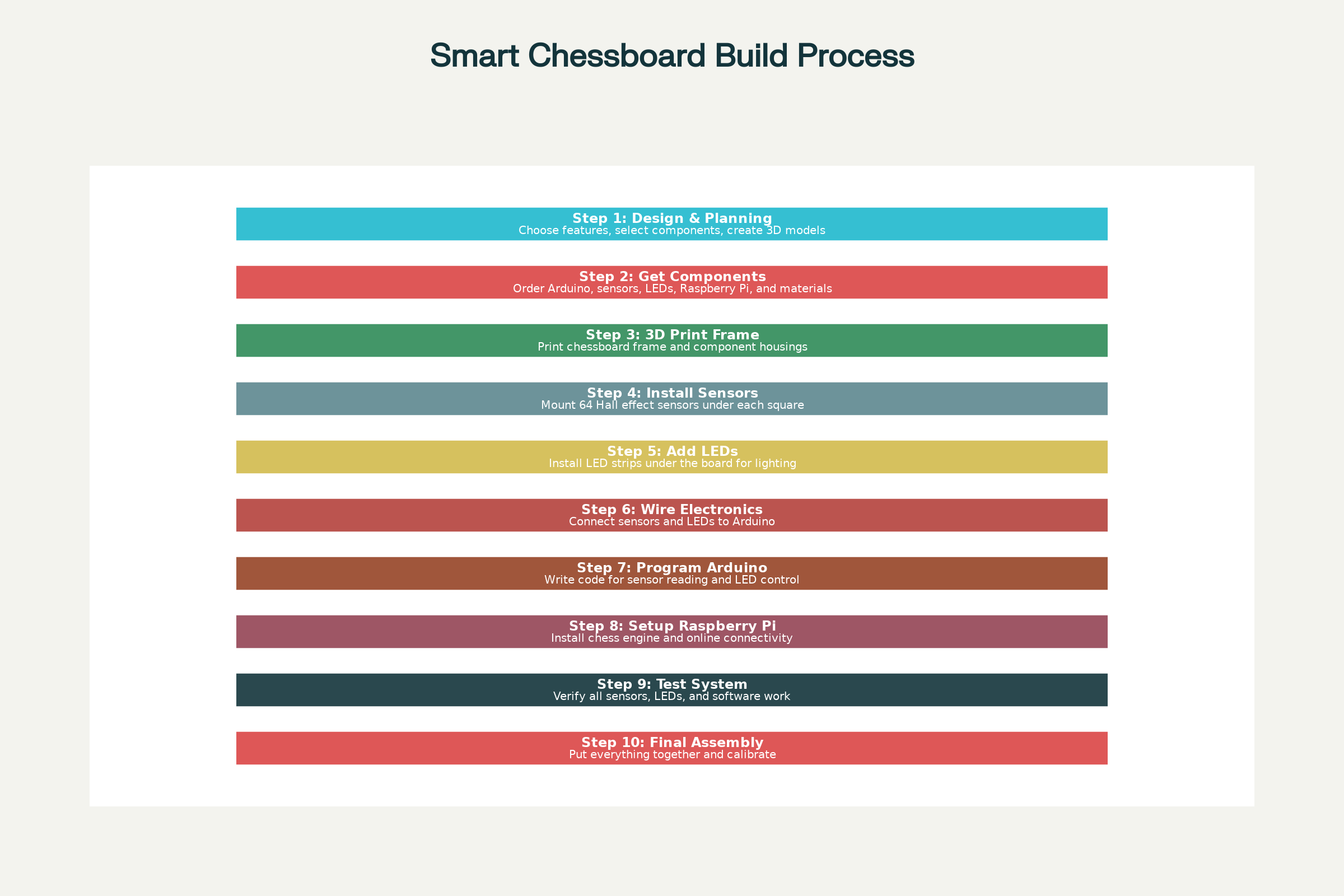
How to Build (Project Flow)
- Frame & Playing Surface
- Print or craft the chessboard frame; design dedicated cavities for sensors and LEDs.
- Install Sensor Array
- Place a sensor (e.g., Hall effect) under each square for detecting piece presence.
- Add LEDs
- Install addressable RGB LEDs under squares for move indication and feedback.
- Control Panel
- Mount tactile buttons and wire them to the microcontroller for user input.
- Wiring & Soldering
- Connect sensors and LEDs into rows/columns and wire to microcontroller pins.
- Electronics Assembly
- Integrate the Arduino for sensor/LED operations; connect to a Raspberry Pi for online play (optional).
- Programming
- Flash Arduino with code to read sensors, control LEDs, and interface with the main system.
- Set up Raspberry Pi with chess engine (e.g., Stockfish) or online chess platform interface.
- Power & Testing
- Power up the system via USB, test for sensor response, LED feedback, and overall functionality.
Skills Required
- PCB/Sensor Layout Design
- Manual Soldering
- Electronic Assembly & Testing
- Arduino Programming (C/C++)
- Raspberry Pi Setup (Python, Linux basics)
- 3D Printing / Woodworking / CAD for enclosure
- Wiring, Drilling, Basic Electronics Knowledge
- Troubleshooting and Debugging
- Sheet cutting and assembly (if using acrylic/wood frame)
- Basic Networking (for remote play features)
Useful Resources
- Super Smart Chessboard Instructables Guide – step-by-step build and wiring diagrams, code, and STL files for 3D printing.
- DIY Machines SmartChess GitHub – code and further resources for the project.
- WouterSchols SmartChessboard – extensive open-source software for hardware interfacing and online play.
- Chess IoT Project (IRJET Paper) – hardware and algorithm design explanations for a sensor-based chessboard.