20251A6: Modular Production System
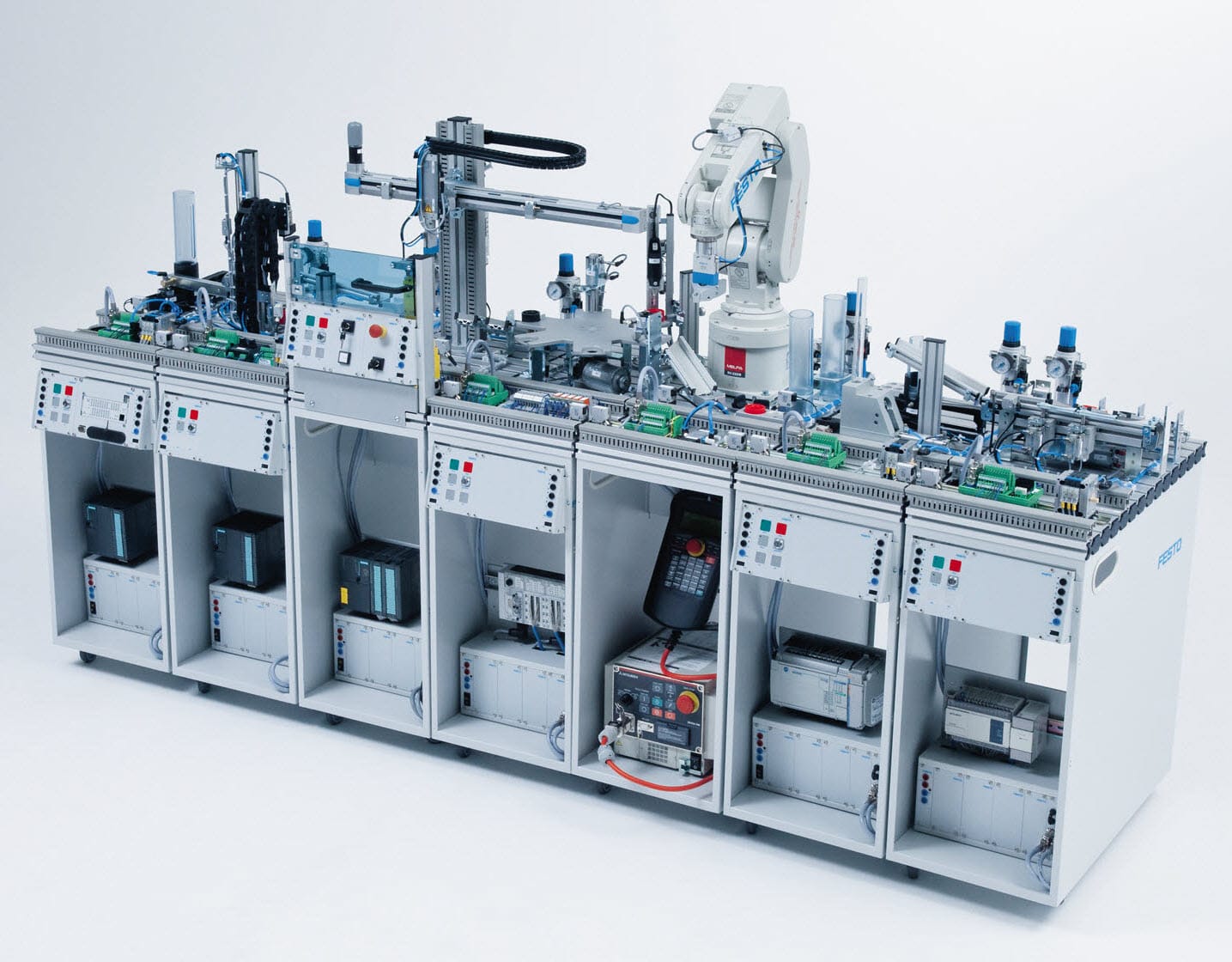
Brief Description & Functionality
Taking the form of a miniaturized production line, the MPS offers an in-depth look into intelligent networking of machines in the production environment, and their work processes. Individual functions of the production or assembly process are grouped into modules from which entire work stations can be accessed in mechatronic units. Each module offers different learning focuses. The modular character of the MPS system enables a flexible and extensive offering of mechatronics and Industry 4.0 learning content. Real industrial processes are the basis for our MPS learning system. Only high-quality industrial components are used that can withstand the rough and tumble of everyday laboratory life.
Components of a Modular Production System:
- Sorting Modules: These modules handle the initial separation and categorization of materials or components based on various criteria like size, shape, color, or material type.
- Assembly Modules: These modules perform specific assembly operations, either manually or with automation, to combine components into sub-assemblies or finished products.
- Handling and Transfer Modules: These modules move materials and products between different modules and workstations, often using conveyors, robots, or other automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
- Control System: A central control system (like a PLC or SCADA system) manages the overall operation of the modular system, coordinating the activities of individual modules and ensuring efficient workflow.
Benefits of modular production systems for sorting and assembly
- Enhanced Flexibility: Easily adapt to different products, production volumes, and market demands by rearranging or adding new modules.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Standardized modules and streamlined processes reduce lead times and accelerate the introduction of new products.
- Cost-Effective Scalability: Minimize initial investment by starting with a small number of modules and expanding capacity as needed.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Automate tasks, streamline workflows, and reduce errors, leading to increased output and optimized resource utilization.
- Better Quality Control: Ensure consistent quality by testing modules individually and maintaining a controlled production environment.
- Sustainability: Reduce waste, optimize energy consumption, and support localized production through efficient use of resources and modular design.
Industrial applications
Modular production systems for sorting and assembly are employed across a wide range of industries, including:
- Automotive: Assembly of vehicle components like engines, chassis, and interiors.
- Electronics: Manufacturing of smartphones, computers, and other devices.
- Logistics and Warehousing: Automated sorting and distribution of packages.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sorting and packaging of drugs and other products.
- Consumer Goods: Assembly of various household appliances and consumer products.
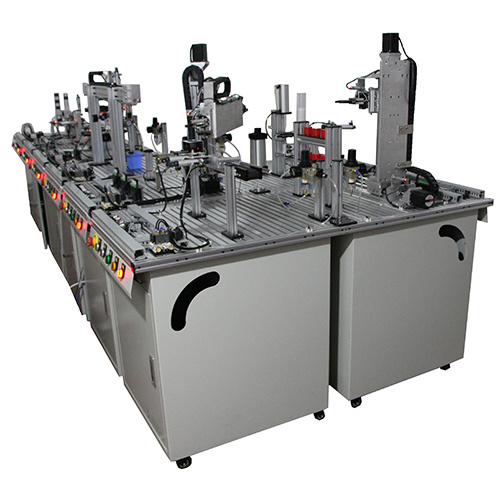
Market Survey

Useful Resources
Skills Required
- CAD design
- Machining on Lathe
- Milling on VMC
- Drilling
- Acrylic sheet cutting
